“How to Troubleshoot PCB: A Comprehensive Guide”
1. How to Troubleshoot PCB: Understand the Purpose of a PCB
Before beginning troubleshooting, it is essential to gain an understanding of your PCB’s purpose and function. Doing this will allow you to both identify problems more quickly as well as potential solutions. Consult manufacturer schematics and documentation; each PCB differs so it is crucial that each troubleshooting project receives special care.
2. How to Troubleshoot PCB: Visual Assessment
A thorough visual inspection should always begin the troubleshooting process. Be on the lookout for visible damage such as burn marks, corrosion or bulges which might indicate potential trouble spots. High-resolution photography is often extremely helpful in pinpointing any irregularities and damages in the initial assessment phase.
3. How to Troubleshoot PCB: Verify Connectivity
With a digital multimeter, check that components are properly connected by conducting a continuity test to see if an electrical path exists between any two points.
4. How to Troubleshoot PCB: PCB Testing
For more complicated issues, PCB testing practices such as In-circuit test (ICT), Automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection, and Functional Circuit Test (FCT) should only be employed by those experienced with PCBs. It is advised to employ one or more of these methods only after making sure all pertinent details have been discussed with you beforehand.
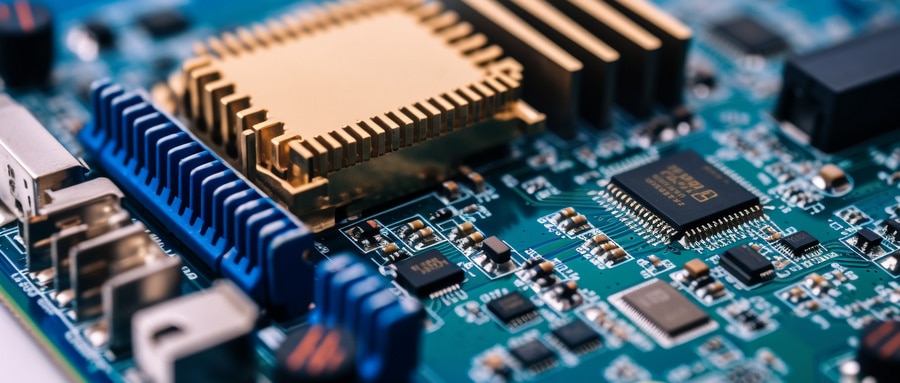
5. How to Troubleshoot PCB: Component Inspection
Components can often be the cause of malfunction. From resistors and capacitors to more intricate integrated circuits (ICs), it’s crucial to systematically inspect them all systematically for any signs of issues, counterfeit components or potential risks.
6. How to Troubleshoot PCB: Engage Professional Services
If your PCB issues continue to persist after undertaking these steps, seek professional services. PCB issues often involve ground planes, internal layers and component level errors which require special tools to troubleshoot effectively.
Troubleshooting PCBs requires technical skill, keen observation skills and an organized approach. We hope that with this guide we will equip you with all of these resources so you can approach PCB troubleshooting confidently.
Future digital electronics will increasingly rely on PCB technologies, making an understanding of PCB troubleshooting essential in this modern, technology-driven world.
Note that safety guidelines must always be observed when handling electrical components. Here’s to a successful troubleshooting experience!
Integrating this guide can significantly enhance your PCB troubleshooting knowledge. Mastering PCB troubleshooting is challenging but highly rewarding – take this chance and dive deeper into its world!
This article serves as your roadmap to mastering troubleshooting effectively and confidently. Prepare to unleash all of your troubleshooting prowess on the complex printed circuit boards found within today’s devices.
